Top 14 Project Management Charts Used by Managers

Project management is an integral part of any business process. Project managers are often facing high stakes, and they need to ensure there are no make-or-break moments in any process. This is where project management charts come in.
According to a recent PMI study, nearly half (48%) of all projects are not completed on time, leading to major financial losses for companies across the board.
However, creating a solid project management plan and using the right project management charts can help ensure that everyone stays on deadline every step of the way.
Read on to learn more about the top 14 project management charts you should be including in your next project plan.
Here’s a short selection of 8 easy-to-edit project management templates you can edit, share and download with Visme. View more templates below:
Table of Contents
- Project Timeline
- Gantt Chart
- SWOT Analysis
- PERT Chart
- Flowchart
- Pareto Chart
- Fishbone Diagram
- Bar Chart
- Pie Chart
- Line Chart
- Work-Breakdown Structure
- Activity Diagram
- Stakeholder Analysis Matrix
- Control Chart
Project Management Chart Overview
Let’s take a quick look at all the project management chart types, their use cases and what kind of projects they’re good for.
| Chart Type | Use Cases | Project Types |
| Project Timeline | Milestone tracking, phase visualization, timeline communication | Event planning, product launches, multi-phase projects |
| Gantt Chart | Task scheduling, dependency mapping, resource allocation, progress tracking | Construction, product development, event planning |
| SWOT Analysis | Strategic planning, risk assessment, opportunity identification | Business strategy, market entry, organizational change |
| PERT Chart | Complex project planning, critical path analysis, probability assessment | Research & development, large-scale engineering |
| Flowchart | Process documentation, workflow optimization, standard operating procedures | Business process improvement, software development |
| Pareto Chart | Problem identification, prioritization of issues, quality control | Manufacturing, service improvement, defect analysis |
| Cause-Effect Chart / Fishbone Diagram | Root cause analysis, problem-solving, quality improvement | Quality management, process improvement, troubleshooting |
| Bar Chart | Comparative analysis, performance tracking, budget reporting | Financial projects, sales analysis, resource utilization |
| Pie Chart | Budget allocation, resource distribution, market share analysis | Financial planning, portfolio management |
| Line Chart | Trend analysis, performance tracking over time, forecasting | Performance monitoring, market analysis, risk tracking |
| Work Breakdown Structure | Project scope definition, task decomposition, deliverable organization | Complex projects, software development, construction |
| Activity Diagram | Process flow, system behavior, user interactions | Software development, business process modeling |
| Stakeholder Analysis Matrix | Stakeholder mapping, communication planning, influence assessment | All project types requiring stakeholder management |
| Control Chart | Quality control, process stability monitoring, variance tracking | Manufacturing, service delivery, quality management |
What are Project Management Charts?
Project management charts are visual tools that support the four phases of project management: initiation, planning, execution and closure. There are several charts that project managers use to help them take care of projects effectively with their teams. Each chart has a specific purpose, and they’re combined to create the perfect system.
Project Management Chart #1: Project Timeline
A project timeline is a graphical representation of a project's deliverables laid out in chronological order.
When you create and share a project timeline for your project, key stakeholders and other team members can get a quick overview of the project using this chart.
Project timelines are important during a project’s planning stage because, as Dr. Pramod Kumar says in his article about the importance of a project’s timeline, “A schedule is more than just dates — it’s the backbone of project success.
What are Project Timelines Best For?
As a project manager, you already know that a project timeline is your best friend when launching a new project. It helps keep a clear organization and gives you better visibility into the project management life cycle.
Furthermore, project charts and layouts also allow you to bulk schedule tasks and provide an in-depth overview of the project from start to finish.
Pros of a Project Timeline Chart
These are the beneficial things you can do with a project timeline. For example, you can:
- List tasks in chronological order
- Show your project’s start date
- View your project’s deadline
- Break the project into phases
Cons of a Project Timeline Chart
While project timelines are valuable tools, they have some drawbacks such as they:
- Need constant updates to stay relevant.
- Don't show complex task relationships well.
- Are too rigid for projects with flexible deadlines.
- May set unrealistic client expectations.
- Fail to account for team availability and workload.
Here's a project management timeline template from Visme to get you started.

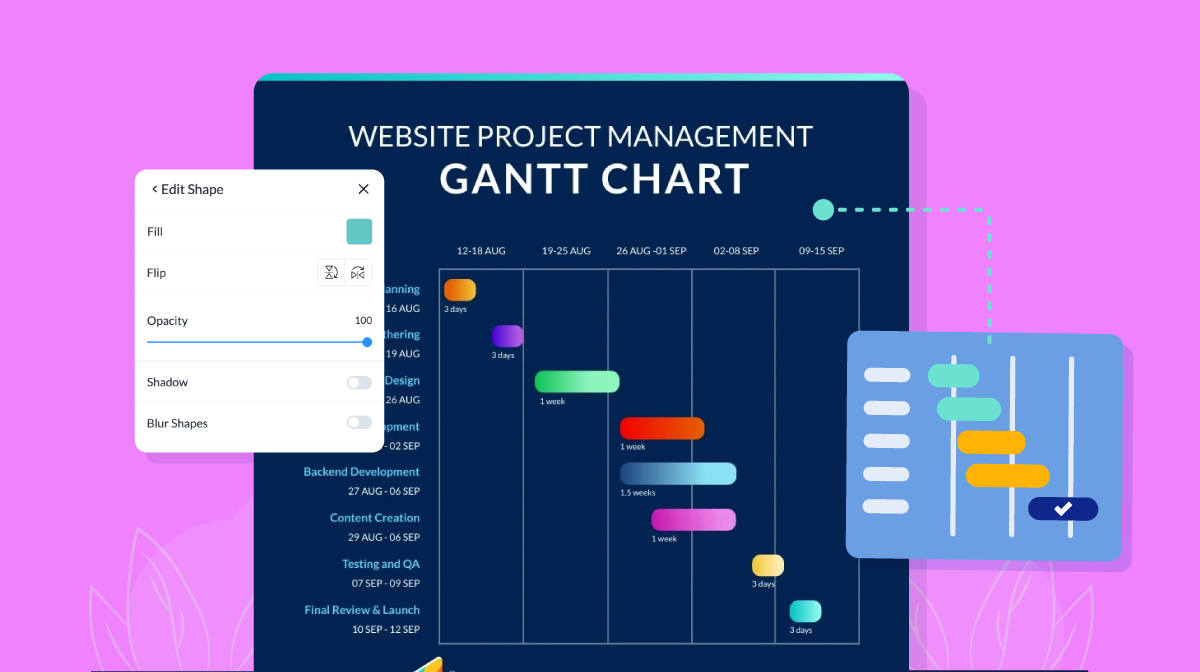
Project Management Chart #2: Gantt Chart
The Gantt chart is one of the most popular and effective project management charts managers use to illustrate a project plan. It's a type of project timeline that uses different-sized bars to display the start, duration, and end of a project.
What are Gantt Charts Best For?
As the project progresses, you adjust the Gantt chart simultaneously to display an up-to-date schedule and inform everyone of the progress. Hence, Gantt charts are one of the best tools for visual task management.
Due to the sheer simplicity and ease of access to real-time information, these charts are an ideal choice for teams to organize their time and schedule effectively. This chart is widely used by marketing, product launch, engineering, and manufacturing teams in various industries. Visme's Gantt Chart Maker makes project tracking a breeze and provides a clear visual representation of every phase of your project.
Keeping things up to date is key, as project manager Amber Caro, CM-Lean, pointed out on LinkedIn about Gantt Charts “On complex projects, publishing and reviewing the sequence bi-weekly or weekly is top priority. This ensures that the clients needs are communicated to the team and that the stakeholders have an opportunity to help plan for the upcoming changes.”
Pros of a Gantt Chart
Here are some of the benefits of using Gantt charts for your project management progress:
- Reduces meeting frequency by providing real-time visual updates.
- Enhances team collaboration through clear handoff points between team members.
- Prevents resource bottlenecks by visualizing workload distribution across different project phases.
- Enables progress tracking with milestone markers.
- Streamlines remote team coordination by centralizing project timelines and deliverables in one view.
- Promotes accountability by clearly displaying task ownership and deadline commitments.
Cons of a Gantt Chart
While Gantt charts are powerful project management tools, they have notable limitations. For example, they:
- Are difficult to maintain for long-term projects.
- Can become cluttered when handling multiple dependencies.
- Tend to be time-consuming to create and update manually.
- Could potentially be overwhelming for team members new to project management.
- Are hard to visualize on small screens or mobile devices.
- Don’t capture quality metrics or project risks.
- May oversimplify complex project relationships.

Project Management Chart #3: SWOT Analysis
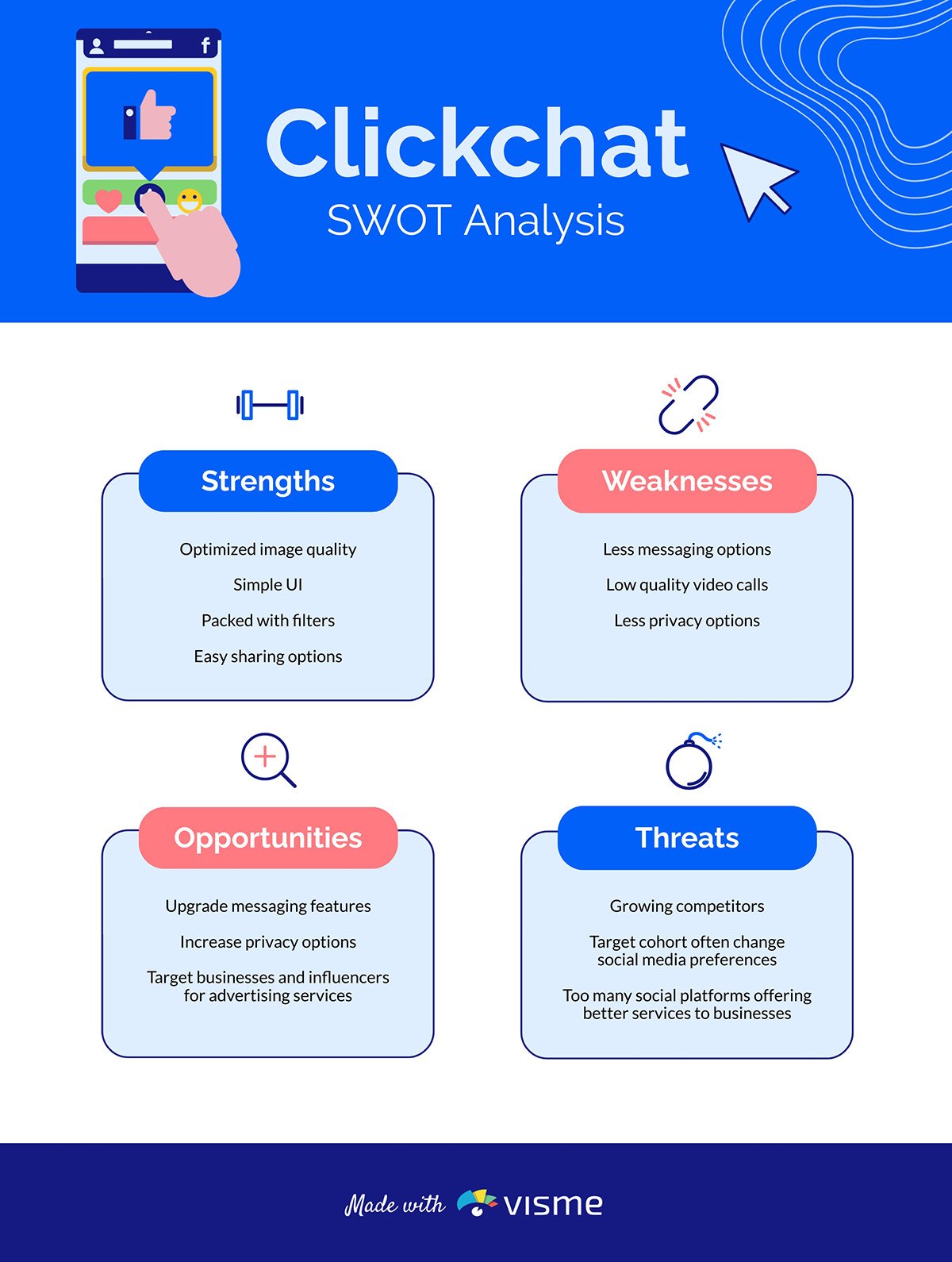
SWOT stands for Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities and Threats. A SWOT analysis gives the project managers and key stakeholders an insight into all the potential risks and opportunities for a project, along with reasons why it's worth it.
What are SWOT Analyses Best For?
SWOT analyses are ideal for strategic planning and decision-making at crucial project stages. They provide a structured framework for evaluating internal and external factors that could impact your project’s success. This analytical tool helps teams identify competitive advantages and potential roadblocks before they become issues.
Pros of a SWOT Analysis Chart
It’s a good idea to implement a SWOT analysis in project management because they:
- Provide a comprehensive evaluation of both internal and external project factors.
- Facilitate strategic decision-making by highlighting key areas of focus.
- Enable proactive risk identification and mitigation planning.
- Help identify untapped opportunities and competitive advantages.
- Promote team alignment through shared understanding of project context.
- Simplify complex situations into actionable insights.
Cons of a SWOT Analysis
While SWOT analyses are valuable project analytical tools, they do have some setbacks. For example, they:
- Can be overly subjective without proper data backing.
- Require regular updates to remain relevant.
- Don’t provide action steps or implementation strategies.
- Can lead to analysis paralysis if they’re too detailed.
- Might miss important factors that don't fit into the four categories.
According to Dr. Gleb Tsipursky, the biggest con of using SWOT analysis in project management is cognitive bias, “Relying on SWOT to inform your strategic plans without accounting for cognitive biases results in appalling oversights that ruin profitable businesses and bring down high-flying careers.”
Look at the SWOT analysis worksheet below. It's a square segmented into four quadrants, each dedicated to an element of SWOT. It will provide a quick overview of a company's position.
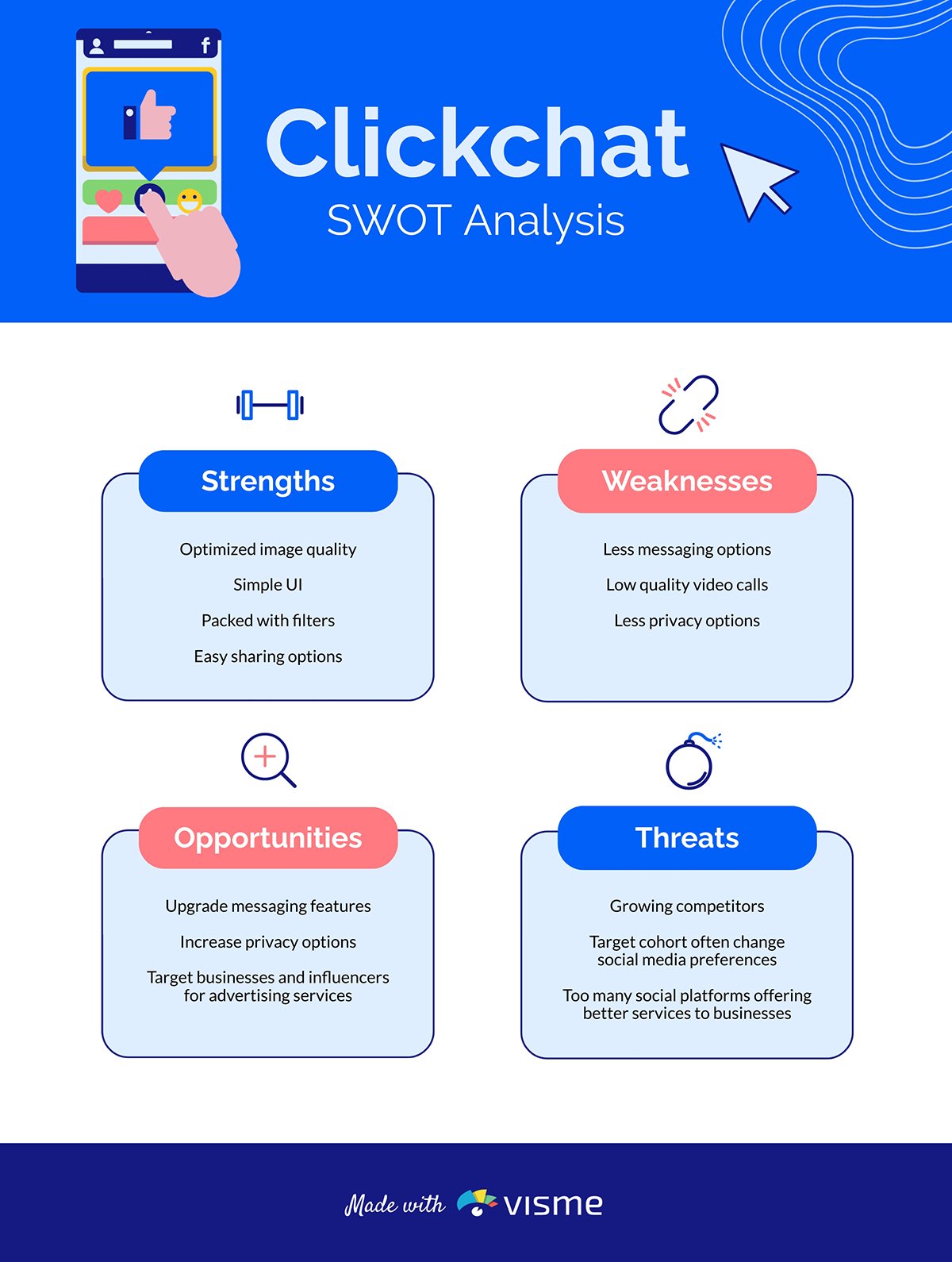
Here are the benefits of using a SWOT analysis in your business:
- Understand your project better
- Identify weaknesses
- Take advantage of your strengths
- Develop goals and objectives
- Capitalize on opportunities
Though you'll need a more advanced solution for complex issues, a SWOT analysis is still a great project management chart to use.
Manage your projects in style
- Create professional branded documents, from project timelines to budgets
- Visualize important project metrics with engaging charts and infographics
- Allow your team to comment, collaborate and move from draft to final format in no time

Project Management Chart #4: PERT Chart
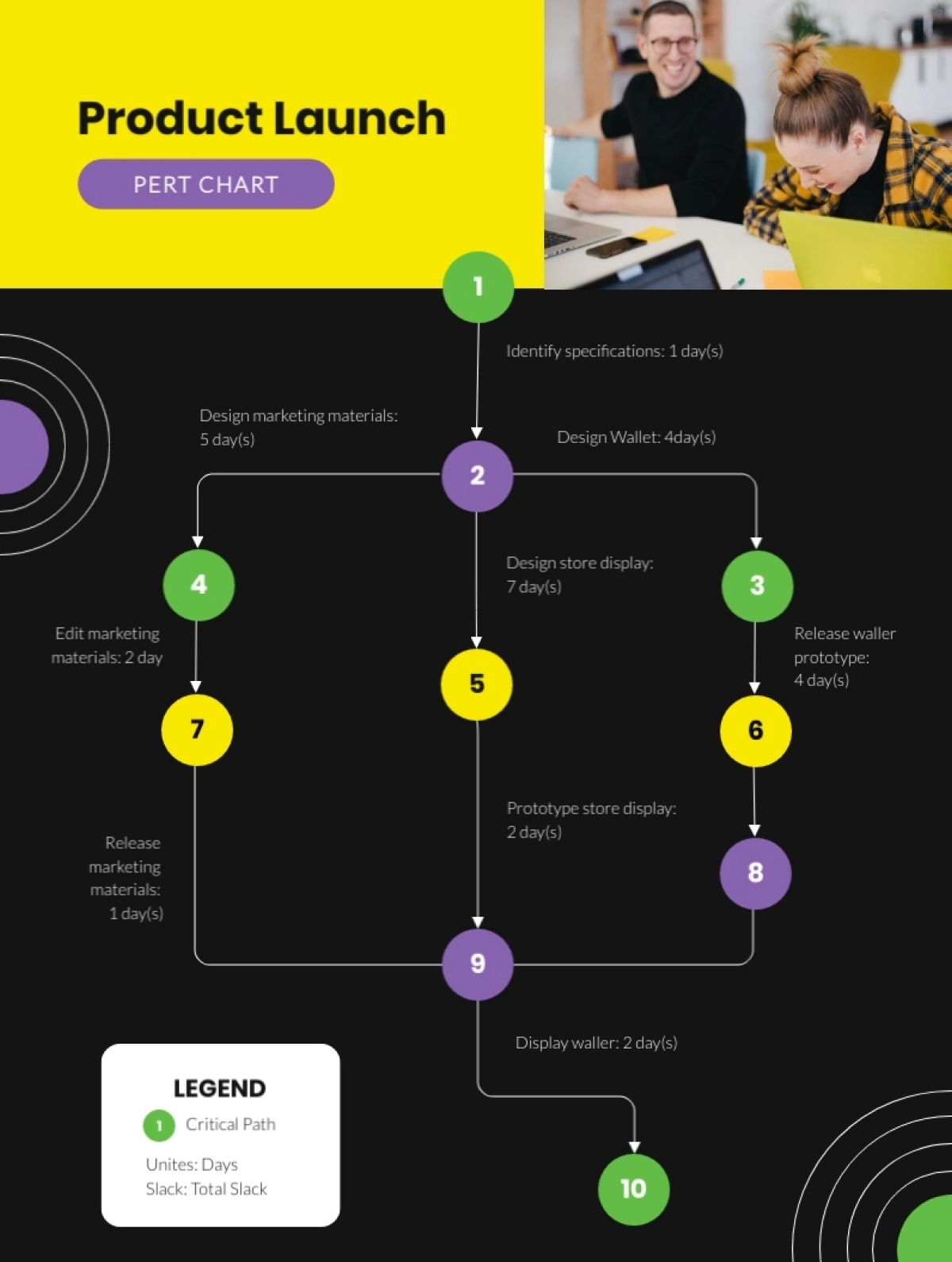
PERT is the acronym for Program Evaluation and Review Technique, and is another famous project management chart that represents the activities and milestones
This chart includes circles and arrows and shows the result in the form of a network diagram. The circles represent the project activities and the arrows depict the progress.
What are PERT Charts Best For?
A PERT chart can help you identify both the critical and non-critical activities of your project.
Furthermore, the PERT chart can display information about the tasks you should take care of simultaneously to speed up the project.
PERT charts are best suited before a project starts, unlike a Gantt chart, which works better during the duration of a project.
Pros of a PERT Chart
There are several key advantages of using PERT charts in project management. Like, for example, they:
- Highlight critical path activities that directly impact your project’s timeline.
- Facilitate better resource allocation by identifying task dependencies and parallel activities.
- Provide flexibility in scheduling by showing multiple path options for project completion.
- Help optimize project duration by identifying opportunities for task compression.
- Support what-if scenario planning for different project approaches.
Cons of a PERT Chart
Regarding the good and bad aspects of the PERT chart, it’s a good idea to consider Senior Airport Infrastructure Engineer, Pablo Roux’s thoughts in a collaborative LinkedIn article and asses if you’re choosing the right chart for your needs.
“The PERT chart, with its ability to visually represent project dependencies, identify critical paths, and calculate slack, is a valuable tool in project management. While it offers several advantages, such as improved communication and risk management, it also has limitations, such as complexity and subjectivity in estimating activity durations.”
So, despite their usefulness in project planning, there are definitely some challenges you might face while using them. For instance, they:
- Can be confusing for stakeholders unfamiliar with the format.
- Are difficult to modify once the project is underway.
- May not account for resource constraints.
- Rely heavily on accurate time estimations.
- Can become unwieldy for large projects with many activities.
PERT chart templates in Visme's graph maker are easily editable and customizable. Here is a PERT chart template that you can use.
Project Management Chart #5: Flowchart
If you're a project manager striving to improve project efficiency, you should give a flowchart a try. It can help you get a clear picture of the processes and work to improve efficiency.
Not convinced? Take Jason Sayen’s word for it, “Flowcharts aren’t the tools you use to run your business—they’re the strategy to optimize it. By identifying knowledge gaps, alignment issues, and software inefficiencies, flowcharts reveal the full picture of your processes. Once you see the process clearly, you can’t unsee it.”
Here are the must-know elements of a flowchart to help you get started with effective design:

Successful project planning and monitoring rely heavily on effective communication. One of the flowchart's primary benefits is that it strengthens team communication by providing a clear visual framework of a complete project or one of its parts.
What are Flowcharts Best For?
There are different types of flowcharts and they are best used to represent a step-by-step process involved in completing a project. They are also essential helpers for determining the right direction to go when something happens during the project’s progression.
Pros of Flowcharts
Here are the key benefits of using flowcharts in project management:
- Enhances process visualization by breaking down complex workflows into clear, sequential steps.
- Facilitates comprehensive analysis through clear identification of decision points.
- Accelerates problem-solving by mapping out potential issues visually.
- Provides a reliable reference for training and process optimization.
- Streamlines communication by providing a universal visual language across teams.
- Supports quality control by standardizing procedures.
- Promotes better decision-making through clear visualization of alternative paths and outcomes.
Cons of Flowcharts
Like any project management tool, flowcharts come with their share of drawbacks. They:
- Can become overly complex and time-consuming for large processes with multiple variables.
- Require frequent updates to remain accurate as processes change.
- May oversimplify complex decisions or interdependencies.
- Make it difficult to show the timing and duration of activities.
- Are limited in showing quantitative information or metrics.
- May not capture exceptions or special cases effectively.
Look at the flowchart template below. The arrows indicate the flow and help determine what comes next depending on an outcome. This example visualizes a product launch process.
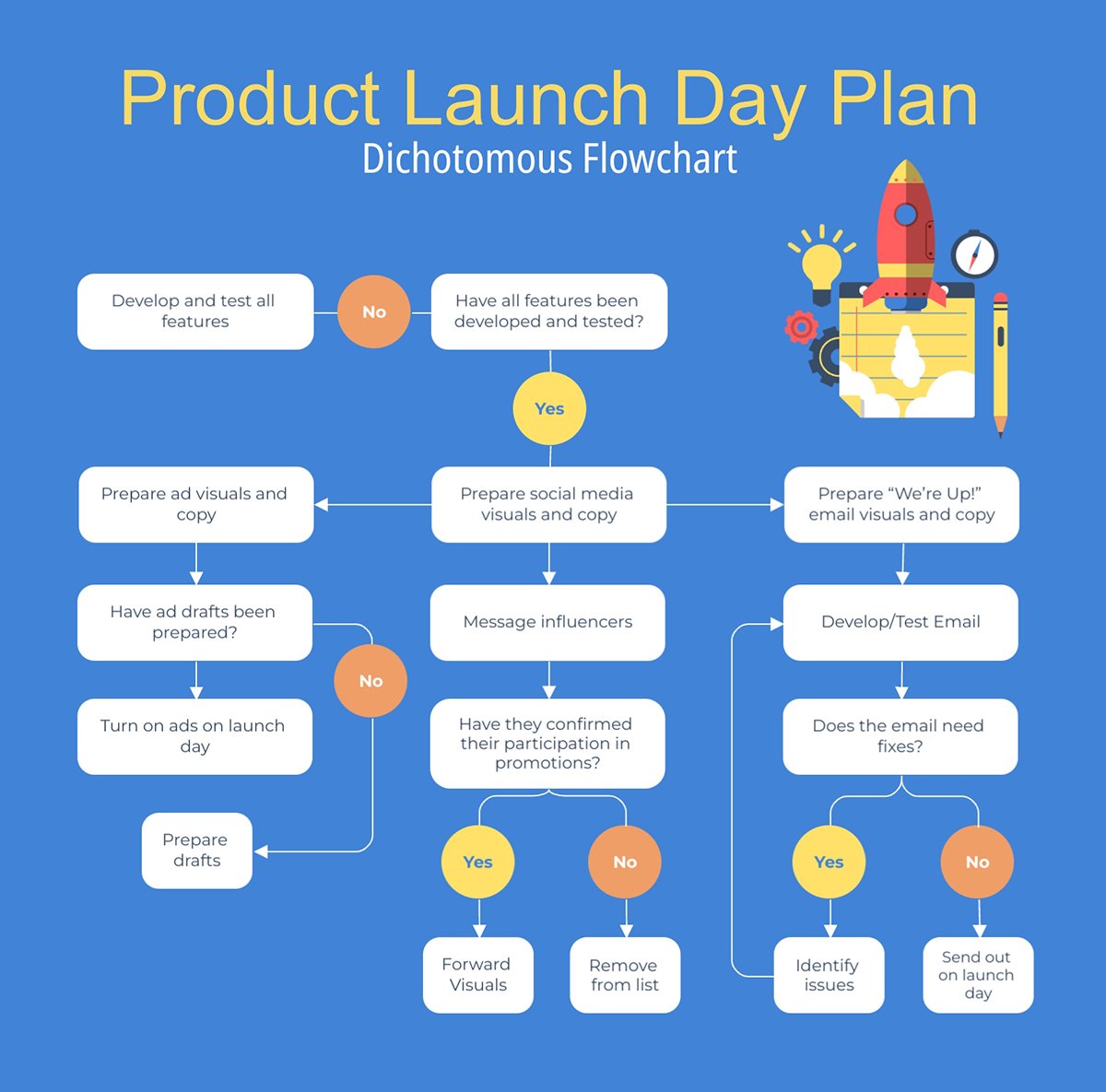
Project Management Chart #6: Pareto Chart
A Pareto chart is a graphical representation of all the defects in a product or the project development process and the frequency of defects.
For project managers, a Pareto chart can be an excellent tool for finding flaws and prioritizing them for improvement.
By combining a bar graph with a line graph, Pareto charts display individual problem frequencies and cumulative percentages simultaneously. Though the chart is handy for Six Sigma analysis, it can fit well into any project management process.
What are Pareto Charts Best For?
The Pareto chart was inspired by the Pareto Principle, which says that 80% of the results are determined by 20% of the causes. By identifying and addressing 20% of defects in your project, you can effectively resolve 80% of your project's problems.
Joe S. business support manager at Key Bank, describes the principle perfectly in one of his helpful LinkedIn posts, “Pareto’s Law reminds us why focus matters. The principle that 80% of results come from 20% of actions is a powerful guide for how we design, prioritize, and execute.”
Pareto charts increase communication and collaboration between team members by providing a clear visual representation of the most significant issues. They are particularly effective for prioritizing problems or defects in manufacturing processes by showing which issues occur most frequently.
In project management they can help by analyzing customer complaints or feedback to identify the most common concerns or demonstrating the relative importance of problems to stakeholders.
Pros of Pareto Charts:
A Pareto chart offers several key advantages, as follows. They:
- Clearly identify the most significant factors affecting a process.
- Provide visual evidence to support decision-making.
- Are easy to understand and interpret for all stakeholders.
- Help focus resources on highest-impact areas.
- Combine different types of data in one display.
Cons of Pareto Charts:
Despite their usefulness, Pareto charts have some limitations you should be aware of. For example, they:
- May oversimplify complex problems.
- Focus only on frequency, not severity or cost.
- Require accurate data collection.
- Can be misleading if categories are not properly defined.
- Are not suitable for analyzing cyclical or seasonal trends.
Here is a Pareto chart template to get you started. The visualization represents a bug frequency analysis for a piece of software, showing how the most frequent bugs represent 80% of the problems. With this information, the team knows what 20% of the bugs to work on first.

Project Management Chart #7: Fishbone Diagram
Also known as cause-effect charts, fishbone diagrams are a visualization tool to logically visualize possible causes of a specific problem in your project. Identifying the potential causes makes it easier to determine the root cause.
Just do what Kaoru Ishikawa, the creator of the fishbone diagram suggests, “Think of at least four factors which influence your problem. See if a shift in one of these causes can give you a different effect to explore.”
What are Fishbone Diagrams Best For?
You can use this chart in the early stages of your project to minimize the issues in a lesser amount of time, uplifting your project's success rate. The most important reason for which you should use this chart is its ease of use.
Additionally, this chart helps you conduct brainstorming sessions that can yield innovative ideas and solutions. However, you need to include all the potential issues in the chart. Otherwise, you might make it challenging to find and resolve a problem during the process.
Pros of Fishbone Diagrams:
When considering the implementation of fishbone diagrams, several advantages make them particularly valuable for problem-solving. Like how they:
- Provide a structured approach to problem analysis.
- Encourage comprehensive examination of all possible causes.
- Help identify root causes rather than just symptoms.
- Facilitate team collaboration and brainstorming.
- Create a visual representation that's easy to understand and reference.
Cons of Fishbone Diagrams:
While fishbone diagrams do help with project management, they come with certain limitations you should consider. For example, they:
- Can become overly complex with too many branches.
- Don’t show the relative importance of each cause.
- May oversimplify relationships between causes.
- Are time-consuming to create and maintain for larger projects.
- Require significant team input for accuracy.
Here’s a fishbone diagram for you to use for your own analysis. This example visualizes the root causes of customer churn, helping a team start to make adjustments and improvements in their processes.
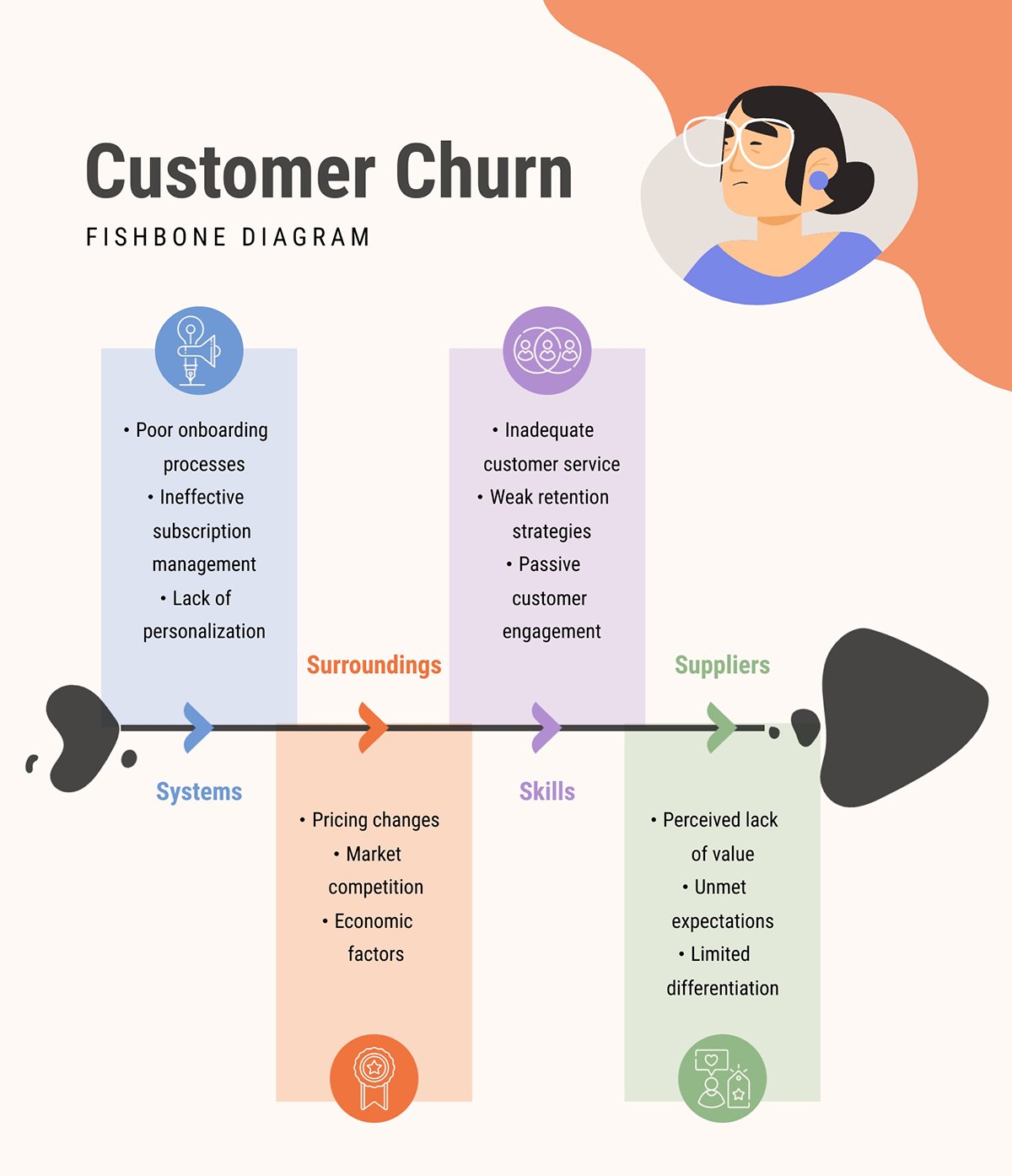
Project Management Chart #8: Bar Graph
Due to their versatility and simplicity, bar graphs are one of the most popular visualizations in project management. Bar graphs are used for visualizing a wide variety of data in the most straightforward way possible.
What are Bar Graphs Best For?
As a project manager, you might need a bar graph to visualize critical information such as your team's performance, efficiency, and quality of work. They are particularly effective at portraying data trends over time, such as resource utilization, task completion rates, or budget allocation across different project phases.
Bar graphs also also practical for showing relative numbers of various categories, helping project managers quickly assess and compare different aspects of their projects, such as team performance, milestone achievements, or departmental contributions.
Pros of Bar Graphs
Using bar graphs in project management has several benefits because they:
- Are easy to read and understand at a glance, requiring minimal explanation.
- Help with comparing quantities across different categories quickly.
- Can handle multiple data sets through grouped or stacked arrangements.
- Allow for color coding and patterns to enhance data differentiation.
Don’t shy away from bar graphs; they are helpful information-sharing tools. As Cole Nussbaumer Knaflic says in his book Storytelling with Data: A Data Visualization Guide for Business Professionals, “Sometimes bar charts are avoided because they are common. This is a mistake. Rather, bar charts should be leveraged because they are common, as this means less of a learning curve for your audience.”
Cons of Bar Graphs
Bar graphs don’t have much going against them, but there are some things. For example, they:
- Could become cluttered when dealing with too many categories or long labels.
- Can be misleading if the scale doesn't start at zero.
- Are not ideal for displaying small value differences between categories clearly.
- Don’t show continuous trends over extended periods compared to line graphs.
Here’s an example bar graph in a template you can use immediately for your own work like a project’s status report or results of a campaign.
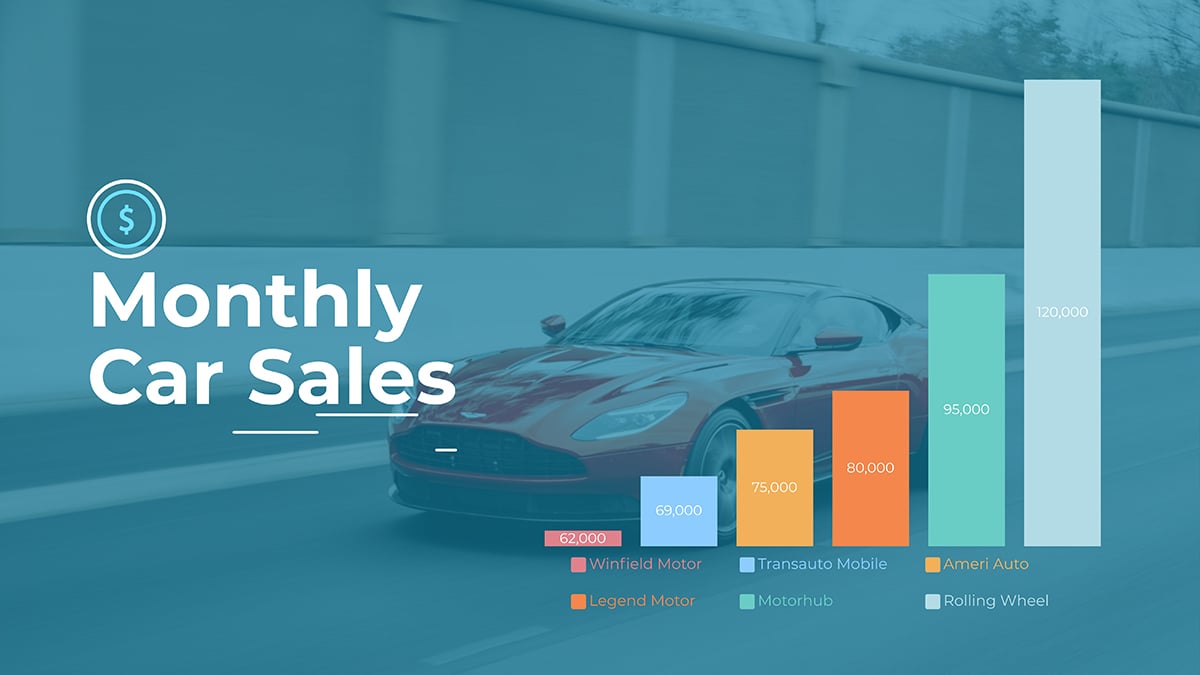
Project Management Chart #9: Pie Chart
As the name suggests, a pie chart is a graphical representation of data in a pie shape. This is also one of the simplest and most popular charts used by project managers. Like bar charts, they can represent different types of data.
What Are Pie Charts Best For?
Due to their circular shape, pie charts are an ideal tool for data segmentation. The primary objective of using a pie chart is to illustrate the different parts that form a collective whole. For example, pie charts can display market share distribution, budget allocations, or demographic breakdowns.
Pros of Pie Charts
There are numerous advantages of using pie charts, such as that they:
- Can represent multiple classes of data.
- Are easy to interpret.
- Need minimal additional explanation.
- Display percentage distributions perfectly.
Cons of Pie Charts
Even though pie charts are easy to use and interpret, they do have some setbacks. For example, Pie charts:
- Are difficult for comparing segments of similar size accurately.
- Become cluttered and hard to read with too many different data sections.
- Can’t effectively show changes over time or compare data across multiple periods.
- Lose color distinction when the number of segments increases.
Here’s a pie chart template you can use for research analysis during your project management processes. This one visualizes time spent on mobile phones according to the activity.
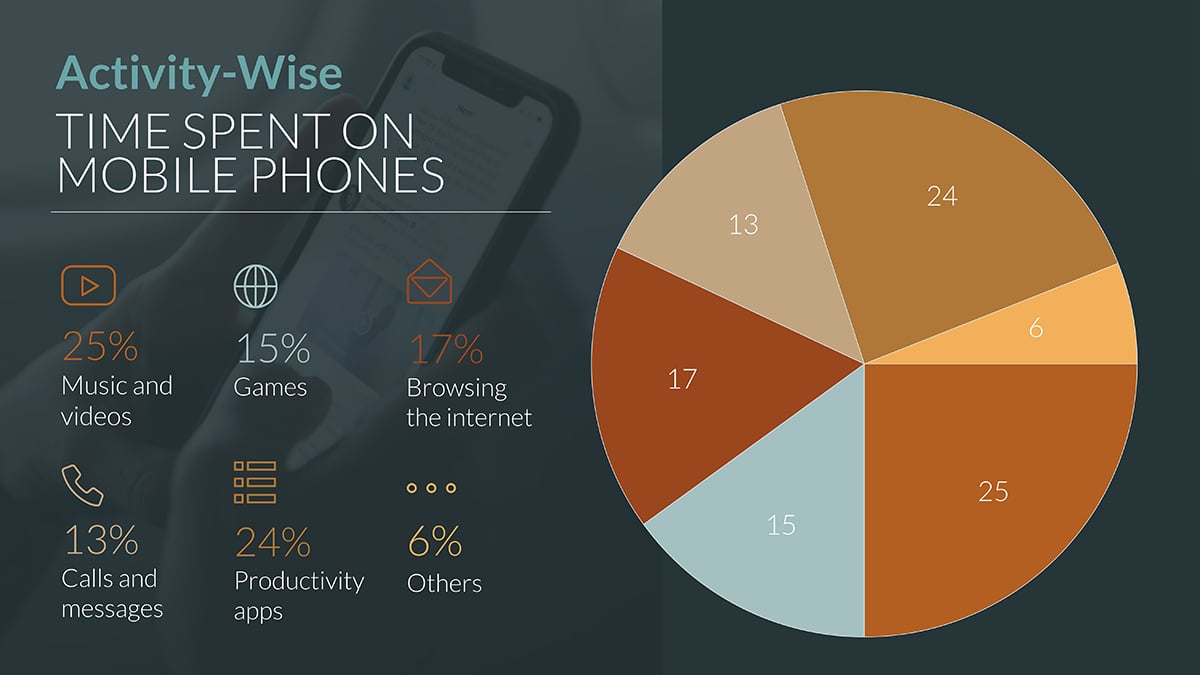
Project Management Chart #10: Line Chart
A line chart is a type of chart that displays the change of data over a specified time. This is one of the most basic types of charts used in finance. Visually, this chart features a continuous line formed over a series of data points.
What Are Line Charts Best For?
You can use line charts in many ways, such as displaying day-to-day changes in performance. Since tracking progress is essential to assess whether a project will be completed on time, this chart is great for project managers.
Other uses for line charts in project management include monitoring budget spend versus time to identify spending patterns and forecast overruns and track key performance indicators (KPIs) over the project lifecycle to spot trends early.
Pros of Line Charts
Line charts are super practical in project management and have many beneficial qualities. Like for example, they are:
- Excellent at showing trends and patterns over time.
- Perfect for showing multiple data series simultaneously.
- Great at revealing relationships between variables.
- Effective at demonstrating rate of change.
- Practical with both large and small datasets.
Cons of Line Charts
Even though line charts are practical for project management, they do have some disadvantages such as that,
- They can become misleading when data points are too far apart.
- There’s a risk of overcrowding when too many lines are added.
- They’re not ideal for categorical data or when there's no logical order between data points.
- Line charts require careful color and pattern choices for accessibility - multiple lines need to be distinguishable for colorblind users
Here's an example of a line chart that would be perfect for your project management.
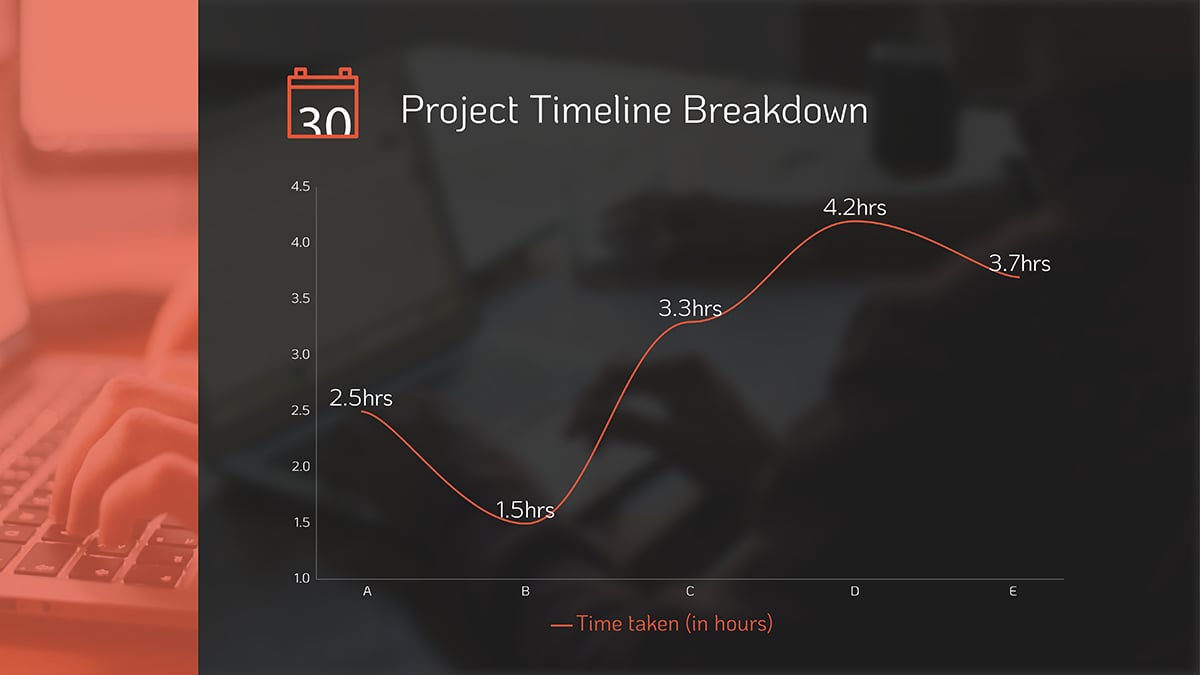
Project Management Chart #11: Work-Breakdown Structure
A work breakdown structure chart in project management is a deliverable-oriented breakdown of a project into smaller manageable sections. It's actually a more summarized version of a business case. Breaking tasks into smaller units is a common productivity technique and a WBS structure is the tool to achieve it.
What Are Work Breakdown Structures Best For?
Though you will not be able to display any stats or figures using this structure, it can help you simplify complex projects. You can formulate a better project plan, schedule and assign tasks, and track their progress to make your project successful.
The visual hierarchy in a WBS provides stakeholders with a clear understanding of project scope and deliverables. It is a common reference point for discussions about project progress, changes, and dependencies. It's a great addition to any stakeholder engagement plan as well.
Made with Visme Presentation Maker
Pros of Work Breakdown Structures?
There are several advantages of using work breakdown structures in project management. WBSs can:
- Create a clear visual representation of all project deliverables, making it easier for teams to understand the full scope of work.
- Help prevent scope creep by clearly defining project boundaries and deliverables at the start.
- Enable better resource allocation by breaking work into manageable chunks that can be easily assigned and tracked.
- Help make accurate cost estimations since each work package can be individually estimated and budgeted.
- Facilitate better risk management by allowing teams to identify potential issues at a granular level.
- Improve project control by providing a framework for measuring progress against specific deliverables.
Cons of Work Breakdown Structures?
No project management charts are without disadvantages, and work breakdown structures are no different. For example,
- Breaking tasks down into too many levels can lead to micromanagement
- They may require frequent updates as the project scope changes.
- It can be challenging to determine the appropriate level of detail for different project components.
- Updates and maintenance can become burdensome if the WBS is too detailed
- There’s a risk of focusing too much on deliverables while overlooking processes and workflows.
Project Management Chart #12: Activity Diagram
When you have complex projects with lots of tasks and subtasks, activity diagrams can help represent the process. Like the work breakdown structure, an activity diagram allows you to divide the tasks into flows.
What Are Activity Diagrams Best For?
With an activity diagram, you can identify the critical path of a project, making it easier to allocate resources. This, in turn, helps significantly reduce your teams' slack time.
Activity diagrams show dependencies for a smoother tracking process. They capture a system's behavior by depicting the events' sequencing through a workflow. The activity diagram is particularly helpful for product development projects.
Pros of Activity Diagrams?
Activity diagrams have several benefits for project management, some of which include:
- A clear visualization of workflow and process sequences.
- A clear display of parallel activities and decision points, helping teams understand where processes split or merge.
- Easy identification of bottlenecks and inefficiencies before implementation begins.
- They help communicate project workflows to stakeholders at all levels, regardless of technical background.
- They work well for documenting both simple and complex business processes.
- They help train new team members on project processes and procedures.
Cons of Activity Diagrams?
There aren’t too many setbacks to activity diagrams. These are the few that are worth mentioning:
- Activity diagrams may not effectively capture resource requirements or time constraints for activities.
- It’s challenging to show the timing and duration of activities.
- They may oversimplify complex processes by forcing them into a linear flow
- Updates can be cumbersome and may require complete redrawing of the diagram.
- They might be too detailed for high-level stakeholder presentations
- Sometimes, they lack the flexibility to show unplanned variations in the process flow.
Here’s an activity diagram template you can use immediately for your project management processes. This one visualizes the state of a student registration process.
By the way, creating activity diagrams collaboratively with Visme is easy. Take it from Vanessa Ware from Vorys, “The nice thing about Visme is that it gives us the ability to all go in, make comments on it, see it, touch it, and go through and see exactly what it's going to look like before it's published."
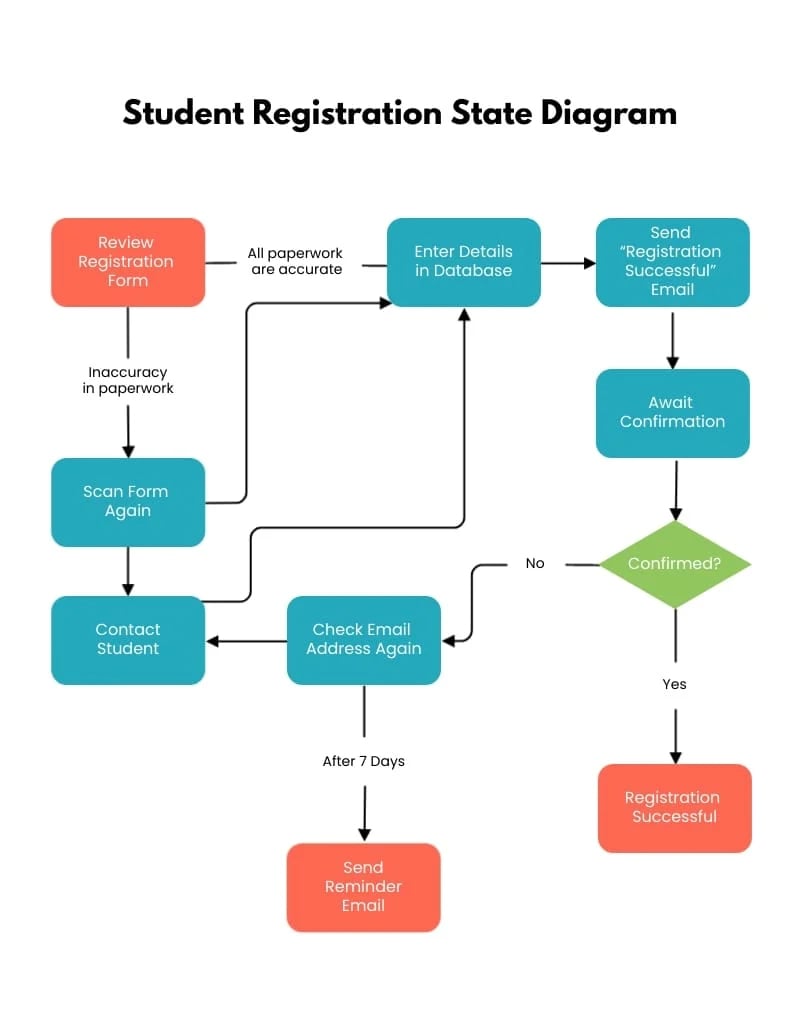
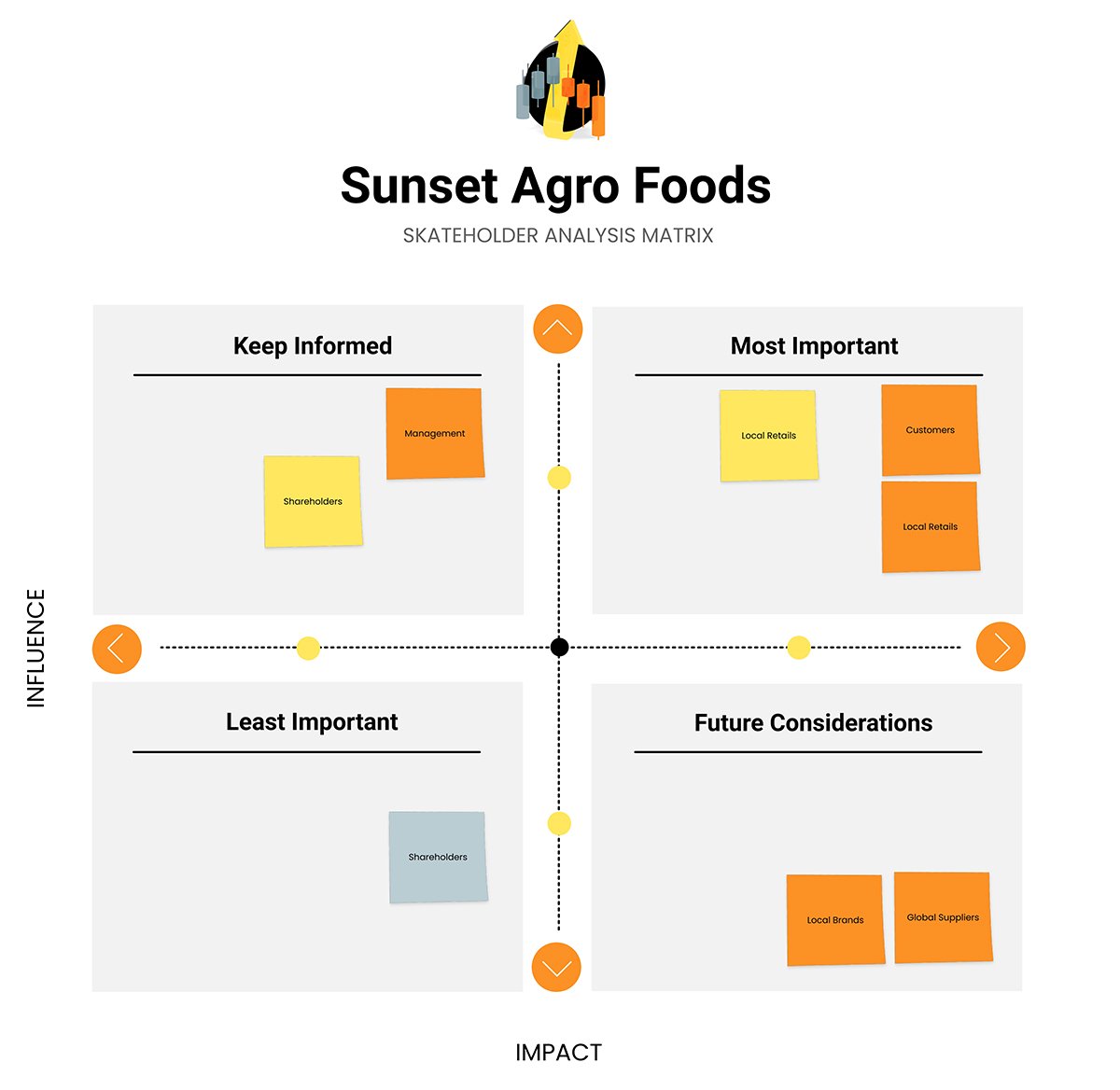
Project Management Chart #13: Stakeholder Analysis Matrix
A stakeholder analysis matrix is a project management tool that identifies key stakeholders and visualizes their engagement for the project's duration.
Your project’s stakeholders are the ones who can support or block your project and become the break-or-make factor. You need to identify the key stakeholders and know where they stand regarding communication and need-to-know status.
If you’re unsure as to how the stakeholder analysis matrix will help you in project management, just read what project manager Thor Dandanell Moensted has to say, “A comprehensive stakeholder analysis is not just a checkbox in the project management process. It is a dynamic, ongoing process that supports decision-making, project direction and ensures that the project aligns with the needs/expectations. Understanding the stakeholder landscape is also a source for potential unclear agendas and underlying cultural challenges.”
What Are Stakeholder Analysis Matrices Best For?
A stakeholder analysis matrix can help you identify, analyze and prioritize your stakeholders. You can use this chart to define:
- The interests of your stakeholders.
- Negative stakeholders and how they affect your project.
- Mechanisms to influence other stakeholders positively.
- Potential risks and issues in your project.
- A strong risk management plan for your project.
Pros of A Stakeholder Analysis Matrix
The stakeholder analysis matrix as a project management chart is very specific for its purpose. So, the benefits are quite detailed. For example, stakeholder analysis matrices:
- Provide a clear visual representation of stakeholder power, influence, and interest levels.
- Help prioritize stakeholder engagement efforts by showing which stakeholders need the most attention.
- Help prevent overlooking important stakeholders who might impact project success.
Cons of A Stakeholder Analysis Matrix
The stakeholder analysis matrix isn’t perfect; it does have some complications. Like, for example:
- It can oversimplify complex stakeholder relationships by forcing them into predetermined categories.
- A stakeholder analysis matrix may not effectively show relationships between different stakeholders or stakeholder groups.
- There’s a risk of bias when assessing stakeholders.
- It can become outdated quickly as organizational dynamics change.
- There is limited space to include detailed information about each stakeholder.
- It’s difficult to represent stakeholders who fit into multiple categories or whose position changes frequently.
Project Management Chart #14: Control Chart
A statistical process control chart can be helpful in project management, as it can accurately represent the changes made in a project.
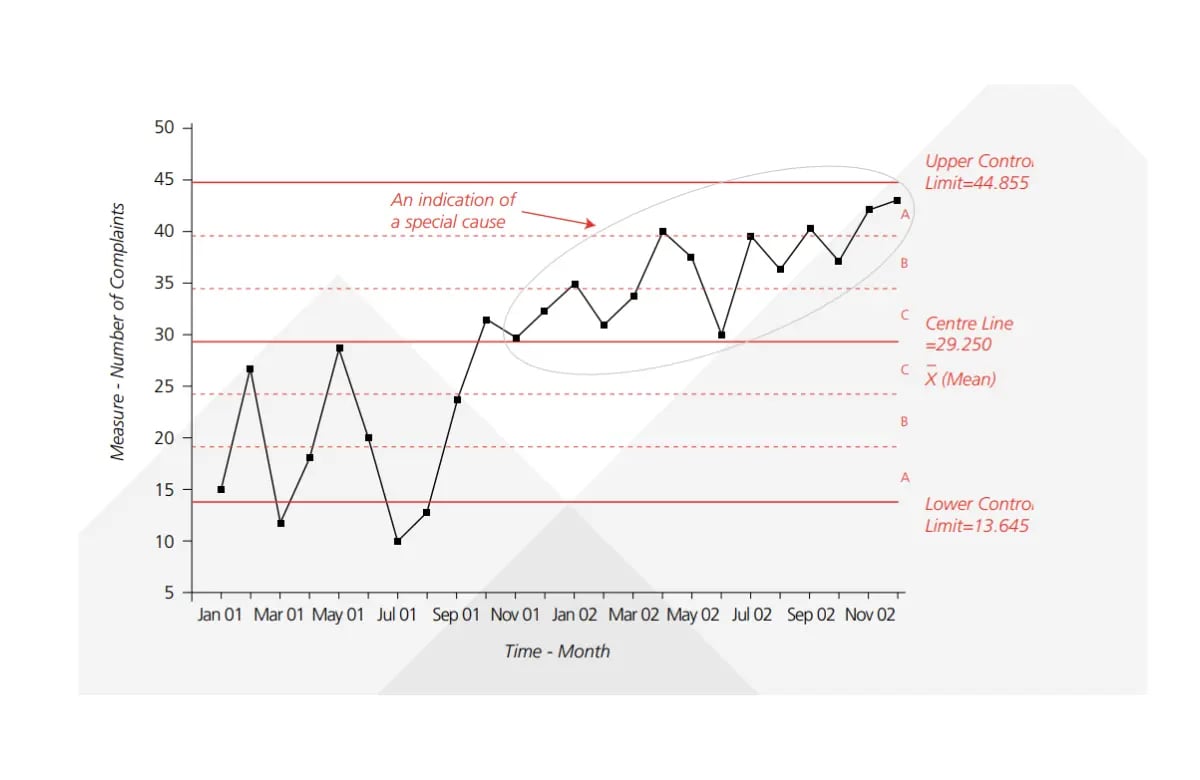
The control chart is a graph with an upper and lower control limit and an average or centerline for process output. As long as the graph line is between the upper and lower control limits, progress is considered fine. When the graph line touches the lower limit or crosses the upper limit, it indicates that the project behavior is undesirable.
Mariusz Dworniczak, PMP explains them clearly in his article about statistical process control charts, “SPC helps to determine if a process is "in control", meaning it is consistent and predictable, or if it is "out of control", indicating that there are issues requiring attention. By using SPC, project managers can prevent problems before they occur by identifying early signs of trouble.”
What Are Statistical Process Control Charts Best For?
This type of chart is best for monitoring your project’s progress. By implementing it, you can identify errors during the early stages. Also, with the help of this chart, stakeholders can quickly develop reliable strategies to improve the project's success rate. With the help of this chart, stakeholders quickly develop reliable strategies to improve the project's success rate.
Pros of Statistical Process Control Charts
In project management, statistical process control charts have several benefits for your quality analysis strategies. For instance, they:
- Provide real-time monitoring of process performance.
- Help distinguish between common cause and special cause variations.
- Are excellent for predicting potential quality issues before they become serious problems.
- Create a visual record of process stability and capability over time.
- Support data-driven decision-making rather than relying on gut feelings or assumptions.
Cons of Statistical Process Control Charts
Statistical process control charts are considerably more difficult to use and interpret than other charts on this list, especially for people who don’t have a statistical background. Therefore, this chart has some setbacks. Like, for example, they:
- Can be complex to set up and interpret correctly.
- Present a risk of false alarms if control limits are not properly calculated
- Can lead to overreaction to normal process variations if not properly understood.
- May be too technical for some stakeholders to understand easily.
Here’s an example of a statistical process control chart.
Project Management Chart FAQs
The best chart for project management depends on the specific needs of your project. But the most common and widely used chart in project management is the Gantt chart.
In project management, the four most commonly used charts are:
- Gantt chart
- Work breakdown structure
- PERT chart
- Pareto charts
Yes, project managers use Gantt charts to visualize project timelines, dependencies, and resource allocation. Gantt charts help keep track of a project’s progress and can be adjusted according to the changes along the way.
The only thing better than a Gantt chart is a combination of project management charts working together in unison to initiate, plan, execute and close a project effectively.
To visualize a project plan, you need some sort of chart on which you can lay out your project’s phases. Some options include a Gantt chart, a flowchart or a project timeline. Likewise, you can also use a comprehensive document that combines different charts along with textual explanations like the project goals and objectives.
A milestone chart is a type of timeline chart that visualizes a project’s milestones. The objective is to visualize a project’s stages according to the milestones that are achieved at the end of each stage. Once one milestone is completed, the project continues on to the next stage.
The chart that shows a project’s stakeholders and their involvement is the stakeholder analysis matrix. This chart is a visual representation of which stakeholders are the most involved in the project’s progress and which aren’t. Knowing this information helps with stakeholder communication.
Create Your Own Project Management Chart
As a manager, you must be familiar with all the helpful project management charts to utilize them for the projects they are best suited to. You can see that all the project management charts mentioned above are tested and proven ones that will help you visualize the project and make correct decisions.
However, you might find it extremely difficult to create these charts, even though you are familiar with them.
So, once you have decided on the type of chart that best fits your project, start creating them using Visme's graph maker. It features hundreds of chart templates to start with across all of the project management charts mentioned above.
Create Stunning Content!
Design visual brand experiences for your business whether you are a seasoned designer or a total novice.
Try Visme for free