
What is Product Management: The Complete Guide for 2026

Research shows that over 40% of all products fail.
The reality is that despite substantial R&D investments, many companies still struggle to develop offerings that truly resonate with their audience.
This statistic isn’t just a number—it represents wasted resources, missed opportunities and potentially severe consequences for businesses. It points to a significant gap between what companies produce and what customers actually want.
But more importantly, it emphasizes product management’s role in determining a company's success or failure.
At its core, product management is about creating value for both the customers and the company. It involves making strategic decisions, market analysis and leading cross-functional teams to develop products that solve real problems while driving business growth.
In this guide, we’ll explore the world of product management, including its roles, processes, challenges and best practices. We’ll also discuss the best product management tools and courses you can use to strengthen your product strategy and execution.
P.S. Short on time? Check out this video for The ULTIMATE Product Marketing Blueprint you’ll ever need!
Product management is an essential organizational function that guides a product through its lifecycle, from ideation and development to product launch and ongoing updates.
It’s a holistic approach that involves understanding customer needs, market demands and business objectives to create products that deliver value to both users and the company.
Anastasiia Tumanova, the Product Director at Niche Publishing House, Expertus, gives us the lowdown on what product management really means in today’s context.
Product Director at Niche Publishing House, Expertus
Effective product management can drive the success and innovation of any company. It’s a strategic process that helps companies stay competitive in rapidly changing industries.
At the heart of this process are product managers, who set the product vision, define features and craft product strategies. They’re also responsible for coordinating with cross-functional teams, including sales, marketing, design and engineering, to bring the product to life.
To better understand product management, it’s helpful to clarify what it’s not.
If you want to know more key differences between product management vs product marketing vs. growth marketing, check out this quick video below:
Product management is essential for several reasons:
From ideation to launch (and beyond), product managers oversee every stage of a product’s journey, ensuring each phase is well-planned and executed.
Consider the lifecycle of a food delivery app. The product manager would:
Leading up to the product launch, they’d oversee beta testing and work on user acquisition strategies. And after the launch, they’d analyze user data to make improvements to the app.
Pro Tip: Use Visme’s product launch checklist templates to streamline your launch process and keep teams aligned on crucial tasks. Customize your checklists by adding unique icons, hi-res images and interactive data widgets, and track progress in real-time. Share the checklist across departments for improved collaboration and a smoother product rollout.
Product managers are often at the forefront of innovation. They track market trends and emerging technologies to drive product evolution.
For example, Maybelline’s product team recognized the challenges customers face while shopping for makeup online and the growing trend of augmented reality (AR) in the beauty industry. In response, they developed the Virtual Beauty Studio, an AR-powered tool that allows users to try on different makeup products in real-time.
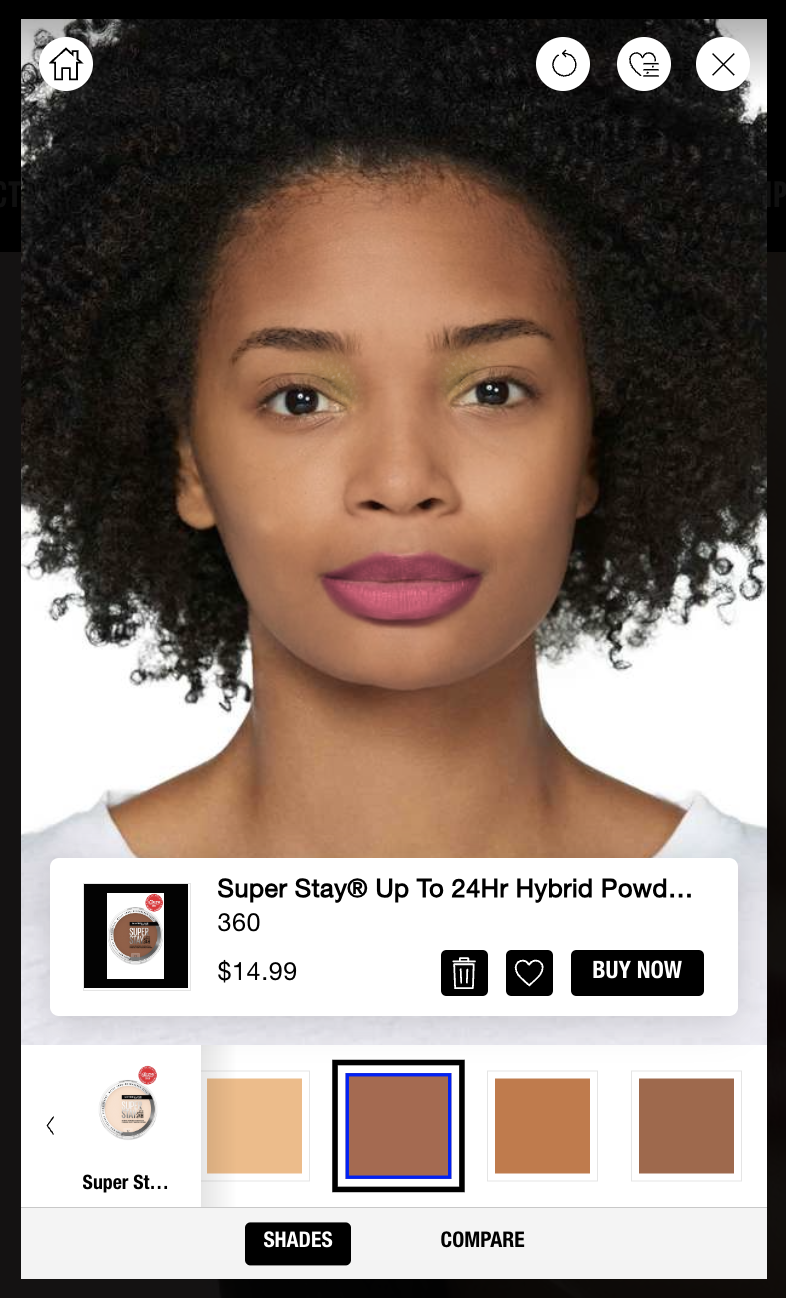
This innovative feature not only enhances the online shopping experience but also helps customers make more informed purchasing decisions, potentially reducing return rates and increasing customer satisfaction.
One of the most important tasks of a product manager is to collaborate with multiple teams and departments to ensure the business and product goals are met.
For example, let’s say a product manager is tasked with developing a new SaaS tool. To make it a success, they’ll need to coordinate with the sales team to understand customer pain points and feature requests, and the customer success team to develop the onboarding process.
“By uniting diverse teams, product management breaks down silos and encourages cross-functional collaboration, leading to more innovative and effective products” shares Anastasiia Tumanova.
The product management and marketing departments can also work together to craft the right product messaging, and the finance team can help determine pricing strategies.
This cross-functional collaboration will not only ensure that the SaaS platform meets technical requirements but also aligns with customer expectations, market demands and overall business objectives.
Pro Tip: Visme offers advanced collaboration features to help you bring multiple teams together to work on projects. Plus, you can keep everything on track by assigning tasks and deadlines and setting up reviews and approvals using Visme workflows.
Product managers act as the voice of the customer within the organization. They conduct market research, analyze user feedback and use these insights to develop products that better meet user needs.
For example, a product manager for a fitness tracking app might advocate for adding a nutrition logging feature after seeing 80% of their user base struggle with diet management or gathering feedback from users, even if it wasn’t initially on the development roadmap.
This customer-centric approach leads to higher user satisfaction and loyalty while driving business growth.
Olha Zaplatynska, Product Marketing Manager at Visme, emphasizes the importance of a targeted and segmented approach to collecting users' feedback.
One of the key roles of product management is to align the product with the overall business goals.
A prime example of this is Amazon’s development of the Kindle e-reader.
In the mid-2000s, Amazon set out with a goal to dominate the book market and transition into the digital space. Jeff Bezos tasked his product team to create a device that would make digital reading mainstream and position Amazon as a leader in e-books.
The result was the first Kindle, launched in 2007. The e-reader sold out in just 5.5 hours, validating the product team’s alignment with Amazon’s business strategy.
Product management helps companies make the most of their limited resources by prioritizing features and initiatives based on their potential impact.
For instance, a product manager for a project management software might choose to allocate more resources to developing an advanced analytics dashboard rather than adding minor cosmetic updates.
This seemingly small decision could significantly enhance productivity for enterprise clients, leading to higher user retention and increased revenue.
Product management is a multifaceted discipline that requires product managers to wear many hats. They typically assume the following roles throughout the product lifecycle:
It’s important to note that the specific responsibilities of a product manager can vary depending on business size. In big organizations, for example, product managers are surrounded by a team of experts, so they spend more time on high-level activities that have strategic impact.
However, in smaller organizations, product managers often have little help. This means they’re likely to spend more time doing things hands-on, such as executing a product strategy and even managing projects.
Product management vs project management is an interesting topic.
While both product managers and project managers play an important part in making products and projects a success, they both have very different focus areas.
Product managers focus on the overall product management strategy and find ways to deliver value to customers and the business over the entire product lifecycle.
Project managers look after the day-to-day execution of tasks. They’re responsible for ensuring projects are completed on time, within budget and to the required quality standards.
Made with Visme Infographic Maker
Product managers take a broad, strategic view of the product. They work with various stakeholders to define the product vision, conduct market research and develop long-term strategies for the product.
Product owners have a more tactical focus, and their role is often found in Agile organizations. Product owners work on a day-to-day basis with the development teams to manage product backlog and make sure the team is focusing on building the right features.
In smaller organizations, these roles may be combined, but in larger companies, they are often separate positions working in tandem to deliver a successful product.
Effective product management requires a combination of soft and hard skills. These product management skills enable managers to successfully bring the product to life.
Here’s a quick breakdown of these skills:
There’s no one-size-fits-all approach when it comes to the product management process. The steps involved, their order and even their emphasis can vary significantly depending on the organization and the nature of the product.
Here are the nine key stages of the product management process:
The first step in the product management process is to identify your customer’s pain points or unmet needs.
Product managers can do this by conducting surveys and interviews, reading what people are saying on social media or monitoring industry trends.
The goal at this stage is to create a well-defined problem statement to gain stakeholder buy-in and guide subsequent product development efforts. The problem statement should address the who (target audience), what (the problem or opportunity), why (the importance) and potential impact (for both users and the business).
Next, conduct a competitive analysis to examine the existing players (and potential future entrants) in the market—their products, features, strengths, weaknesses and pricing strategies—to identify areas where your product can shine.
Product managers can do this by using a combination of methods such as SWOT analysis, product testing and customer feedback analysis. The aim here is to find out whether direct and indirect competitors pose a significant threat or if there are opportunities to outperform them. Your competitor analysis can also be complemented with a business case template if you need to persuade shareholders to undertake a product marketing project.
Check out these competitor analysis templates to create one for your product management needs. Enhance your documents with photos from Visme’s built-in stock photo library or upload your own assets.

If you can’t find the perfect image, use the AI Image Generator to create graphics based on prompts. You can also touch up, resize, upscale, unblur and remove backgrounds from your images using our AI Image Editing tool.
Once the problem is defined and the competitive landscape understood, the next step is to research potential solutions. Next, evaluate them against multiple criteria, including technical feasibility, market viability and business model fit.
Product managers can do this by conducting cross-functional brainstorming sessions, analyzing successful solutions in similar markets and engaging in design thinking workshops. The aim is to create a shortlist of potential solutions, each with a high-level concept description.
Prototyping is an important step in the product management process. It allows product managers to test all their product-related assumptions and make data-driven decisions about the product.
Product managers collaborate closely with designers and engineers to create prototypes of varying fidelity—from low-fidelity paper sketches and wireframes to high-fidelity interactive mockups. The goal is to create something tangible that users can interact with and provide feedback on.
Once a prototype is ready, conduct focus groups and usability testing sessions to identify potential issues, validate key features and uncover new insights about user needs.
It’s important to note here that prototyping and validation is not a linear process but a cyclical one. Testing should continue until there’s a solution that resonates with the target market.
Pro Tip: You can build prototypes or mockups for your website or app using Visme’s wireframing tool. Use pre-made wireframe templates and drag-and-drop elements onto your canvas, and work with your team to visualize product concepts before sending them for development.
The Minimum Viable Product (MVP) represents a significant milestone in the product development journey. It’s the simplest version of the product, released to a select group of users to gather real-world feedback.
Dropbox, for example, initially launched as an MVP to validate its concept of cloud storage and collaboration, which allowed it to gather valuable user insights and iterate on the product.
Drew Houston, CEO of Dropbox, said that the video drove hundreds of thousands of people to their website and their waiting list went from 5,000 people to 75,000 people overnight.
The MVP development process often follows Agile product management methodologies, with product managers playing an important role in sprint planning, backlog grooming and prioritization. They act as the bridge between the development team and stakeholders to make sure that the MVP meets both business and product goals.
Once the MVP is in the hands of users, product managers must work closely with customer support teams to find out what they’re saying about the product.
This phase is especially crucial because customer feedback often leads to product changes. So product managers must carefully analyze each user comment and ensure it aligns with the product strategy or is feasible to implement.

Product Marketing Manager at Visme
Now that you’ve incorporated customer feedback into the product, it’s time to create a product management roadmap and define its long-term goals.
The product strategy serves as a high-level plan that outlines how the product will evolve to achieve business objectives. It typically includes:
With these elements in place, product managers can develop a product roadmap to visualize the strategy over time.
Pro Tip: Use Visme’s roadmap maker to get all your product stakeholders on the same page. You can start from scratch, or better yet, browse our library of roadmap templates to find a design you like.Remember, the product strategy is not set in stone. It should be regularly reviewed and adjusted based on market feedback and changing business priorities.
Next, it’s time to put your product strategy into action.
This step of the product management process requires managers to wear multiple hats. They have to collaborate with different teams, manage resources, make quick decisions and ensure everyone is aligned with the product vision.
At this stage, it’s common for unexpected challenges to pop up. So product managers will need to stay flexible and do all they can to keep the product on track. This might involve adjusting sprint plans, reallocating resources or refining the product strategy as a whole.
Launching a product is not the end of the product management process but rather the beginning of a new phase—continuous improvement.
Product managers will need to observe social media and review sites for user sentiment and monitor KPIs like user adoption rates, engagement levels, conversion rates and churn rates to track product performance. The insights will then be fed back to the product development cycle to improve the product.
In this way, product management becomes a continuous loop of learning, improving and evolving the product to better serve users and meet business objectives.
A product manager’s approach to handling B2B and B2C products is similar in many ways. In both cases, they must define product strategy, understand customer needs, collaborate with multiple stakeholders and drive business growth.
However, there are subtle differences in how these principles are applied.
Made with Visme Infographic Maker
B2B products are more complex than B2C products, with longer sales cycles and multiple decision-makers. This means there’s a difference in sales channels. B2B relies more on human reps to build relationships and articulate product value, while B2C focuses more on automated processes and marketing.
Another key difference lies in the target audience. B2C companies often have a large and diverse user base with various personas. And in most cases, the buyer is typically the end user.
B2B companies, however, are often focused on particular ICPs, segments and industries. Additionally, the decision-maker is not always the end user. This means B2B product managers need to have deep industry knowledge and understanding of both their buyers and users.
Pricing a B2B product is also a bit trickier than pricing a B2C product. For B2B buyers, the most important thing is a high ROI, so you need to back your price with a solid cost-benefit analysis. B2C products, however, often vary greatly in price depending on how they’re marketed and their emotional connection with the audience.
Finally, B2B product management is less flexible than B2C product management in terms of changes and updates. For example, you could probably upgrade a B2C product without significantly disrupting your customers’ lives. But you need to communicate your plans to roll out B2B product changes well in advance so you don’t interrupt your clients’ processes or negatively impact their business.
Product managers face several challenges in their roles. Here are five common challenges and strategies to overcome them:
Made with Visme Infographic Maker
Product teams often struggle with information silos, which are caused by poor communication practices and disconnected workflows across departments. This often leads to duplicated efforts and also risks creating a fragmented product experience for users.
Balancing stakeholder requests, user needs and technical constraints to decide which features to build next is a constant challenge for product managers.
Figuring out what features matter most is a big deal in product management, and Olha explains how complicated it can get.
According to Olha, using the RICE framework can provide some structure, but it also has limitations, especially when assumptions about impact and confidence go awry. Another important bit is effort: how many man hours, how long, essentially how much it's going to cost to implement the feature."
Another way to decide which features are most important, as Olha suggests, is through testing.
Another common challenge faced by product managers is to collect meaningful customer feedback and translate it into actionable product improvements. Failure to do so can result in misaligned product development, missed opportunities for innovation and ultimately, a product that fails to meet user needs and market demands.
Ensuring the product continues to meet the market needs is another ongoing challenge that product teams face. Failing to do so can lead to declining user engagement, increased churn rates and ultimately, product failure.
Andrey Ayriyan, Product Manager at Visme, emphasizes that product market fit is not just a problem for startups but also a goal for established and growing organizations.
Product Manager at Visme
“We scrutinize feature demand trends to understand which features are most in demand. This allows us to stay relevant and offer our clients what they really need.” shares Andrey.
Here are some other strategies that Andrey suggests for businesses to find and maintain market fit.
Even if your product is good, if users don’t immediately grasp its value and functionality, there will be an immediate disconnect between them and your product. This could lead to high early-stage churn, negative word-of-mouth and stunted growth.
For product managers, creating an intuitive onboarding process and encouraging adoption can be challenging because it requires a deep understanding of different user segments.
Whether you’re managing a small product or a complex enterprise solution, you need product management tools in your tech stack to streamline workflows and boost productivity. Here are five of the best product management tools to consider:
Jira is a powerful project management tool that’s particularly famous with companies that follow Agile methodologies.
It offers customizable workflows, 1,000+ third-party integrations and is ideal for managing product backlogs, sprint planning, issue tracking and release management.
Jira offers a free-forever plan for up to 10 users. Their paid plans include:

Next on our list of the best product management software is Basecamp—a simple, yet powerful project management and team communication platform.
It offers a clean user interface, simplified workflow management and integrated collaboration tools, making it a one-stop-shop for teams looking to simplify their project management processes.
Basecamp doesn’t offer a free plan, but they do offer a 30-day free trial for both its paid plans. They are:
ProductPlan is a professional roadmapping tool that enables product managers to visualize and communicate their product strategy effectively.
It offers intuitive roadmap creation tools, robust collaboration features and multiple integration options, making it ideal for teams looking to align stakeholders and track product progress.
ProductPlan doesn’t publicly share its pricing. You have to contact their sales team for a custom quote. However, their paid plans include:
Asana is a popular work management platform that helps teams effectively organize, track and manage their work.
Its powerful features, like customizable workflows, task dependencies and timeline views make Asana an ideal pick to stay on top of all your product-related tasks.
Asana offers dedicated plans for both individuals & small teams and businesses & enterprises.
Individuals & small teams
Businesses & enterprises
airfocus is a modular product management platform that adapts to your specific needs. Whether you’re developing a new mobile app, designing a fintech solution, or innovating in blockchain technology, airfocus offers flexible, mix-and-match modules to suit your workflow.
Its customizable frameworks and powerful prioritization tools make it an excellent choice for product teams of all sizes seeking a data-driven approach to product management.
airfocus doesn’t have a free plan but offers a 14-day free trial with no credit card requirement. The paid plans are as follows:
We’ve covered the product management process in detail and how to avoid some common challenges product managers face in the previous sections. But let’s talk about how you can take your product management strategy from good to great.
Here are some tips to keep in mind:
Agile project management methodologies like sprint planning and daily stand-ups break your work into smaller, manageable chunks so you can adapt to change and deliver value faster.
Use Visme's agile templates to work together with your team on things like scrum and kanban boards, trackers, retrospectives and more. Keep everything on brand using Visme’s AI-powered branding tools.
Make decisions based on what your users need and want so you can build a product people will actually use and love. Regularly talk to your customers.
Conduct surveys, user interviews and usability tests. Do everything it takes to keep your product strategy customer-centric.
Using concrete information like data to guide your product strategy reduces risk and helps you maximize your resources. Have a system in place for tracking and analyzing data at every step of the way.
For example, use analytics tools like Google Analytics or dashboards to understand how users are interacting with your product. Use Visme to create visual reports to share key metrics and findings with your team to keep everyone on the same page.
This refers to maintaining a prioritized list of features and improvements for your product. It keeps your team focused on what's most important and helps you plan for the future.
Make sure to regularly review and update your product backlog with your team. You can create a visual roadmap in Visme to communicate your product's direction and priorities to stakeholders.
Wondering how to get into product management? Upgrading your product management skills is essential for entering the field, driving innovation and staying competitive.
In this section, we’ll look at some specialized courses that offer practical knowledge and skills to help you create, launch and manage successful products.
Digital product management can be different from physical product management. This course is designed to set product managers in the digital and tech space up for success.
You'll dive into topics like managing digital product lifecycles, generating product-qualified leads, improving user experience with onboarding, activation and gamification strategies, and making smart decisions based on data.
Successful product managers embrace new technology to keep their products relevant and competitive. This includes using AI in various aspects of the product development process.
This specialized course will teach you how to use AI for product management and drive business growth, increase product value, and even build AI-powered tools and features.

The Project Management Professional (PMP) certification from PMI is a globally recognized credential that focuses on project management principles and practices.
This course can help product managers launch successful products by incorporating project planning, execution and management best practices. For example, they’ll be better able to deliver products on time and within scope as well as meet quality standards.
The primary job of a product manager is to deliver successful products and meet business goals. To do this, product managers have to oversee the entire product lifecycle, from ideation to launch and beyond, define product vision, create a strategy, prioritize features and work with cross-functional teams.
The 5 P’s of product management are Product, Price, People, Place and Promotion. These 5 P’s form a framework that guides product managers in key decision-making areas throughout the product lifecycle, from development to market positioning and sales strategy.
The 7 stages of product management are identifying the problem or opportunity, conducting market and competitive analysis, creating prototypes, building an MVP (Minimum Viable Product), setting product strategy, driving execution and analyzing post-launch data.
Product management has several types of product managers. The most common ones are the technical product managers, marketing product managers and business product managers.
The product management lifecycle involves monitoring market trends, improving or updating the product, adjusting marketing and pricing strategies, planning for product retirement and innovating to extend the product’s life.
Project management is about getting specific tasks done on time and within budget. It’s the “how” and “when” of making things happen. Product management, on the other hand, is all about the big picture. It’s figuring out what to build and why, based on what customers want and what’s good for the business. While project managers execute plans, product managers shape the overall vision and strategy for a product throughout its life.
Generally, product managers earn more than project managers due to their strategic role and broader responsibilities. Having said that, salaries are largely dependent on the manager’s experience, industry and location.
Product managers typically oversee product owners, product development teams and UI/UX designers. They also collaborate closely with marketing, sales and customer support teams to align product goals and strategies.
Product management can drive business growth and success by guiding products from ideation to development to launch and beyond.
Remember, successful product managers balance strategic thinking with hands-on execution. This means they adapt quickly to market changes and leverage the right tools.
Visme stands out as an excellent platform for product managers and other business professionals. You can easily create product roadmaps, proposals, whiteboards, presentations, reports, assets, plans, diagrams and more using templates and advanced design tools.
Beyond design, Visme offers integrations, collaboration features, custom branding, interactivity, data visualization and AI-powered tools to help you generate text, images and even custom AI documents tailored to your unique needs.
Find out more about how Visme can elevate your product management strategy and become an integral part of your business tech stack. Sign up for free or schedule a demo today.
Design visual brand experiences for your business whether you are a seasoned designer or a total novice.
Try Visme for free